Cat 7 vs Cat 8 Cables: What’s the Difference?
Supposedly, you have to install data cables for your newly built house, but you don’t know about them. And we all know that the variety of ethernet cables available in the market, such as Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat8, and so on, can get overwhelming.
So, if you are selecting a cable for your place, it is important to understand its features and capabilities.
Presently, Cat 7 and Cat 8 cables are marking their presence in the market with their efficiency and compatibility with other ports. Complicated questions are bound to arise, like whether using Cat 8 with standard Cat 7 would work or not.
To answer such questions before they arise, let’s understand Cat 7 and Cat 8 in detail, including their main differentiating point.
A Brief about Cat 7 and Cat 8 Cables
Let us understand both the cables in a brief.
Cat 7 Cables:
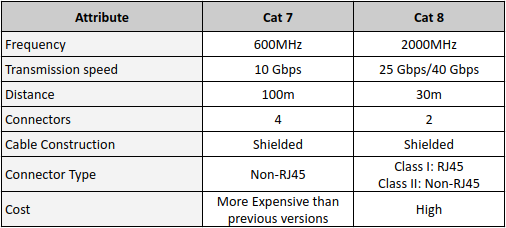
Category 7 cable, known as a Cat7 or Cat-7 cable, is used to cable the infrastructure of Gigabit Ethernet. It offers up to 600MHz—a perfect choice to cable your smart home. After cabling, you can even check for automation ideas.
It supports high-speed ethernet communication up to 10 Gbps. These are backward compatible with Cat6, Cat5, and Cat5e categories. 
It provides a 100-meter 4-connector channel with shielded cabling. They require twisted wires to become a full shield system. Such systems are screen-shielded twisted pair (SSTP) or screened foiled twisted pair (SFTP) wiring.
It eliminates alien cross-talk with improved noise resistance. It allows users to get higher speeds with longer cables.
Cat 8 Cables:
Category 8, Cat8 cable or Cat-8 cable, is an ethernet cable, which is a different type of cable standing apart from the previous cables. It supports a frequency of up to 2GHz(2000 MHz). It is limited up to the 30-meter 2-connector channel. It requires shielded cabling as well. The major point to consider is that it can support a speed of 35 Gbps or 40 Gbps. Overall, its physical appearance is similar to lower category cables. They terminate in RJ45 connections or non-RJ45 connections. It is compatible with all its backward versions. You can use it with the standard connectors of previous versions, such as Cat-7.
Cat 7 vs. Cat 8 Comparison
While comparing these cables transmission frequency and cabling length are of great importance. Here is the detailed comparison:
Performance:
Cat7 cable offers performance up to 600 MHz, whereas Cat8 offers up to 2000 MHz
Cabling Length:
The maximum cabling length of a Cat 7 network is 100m with 10 Gbps, while Cat8 is limited to 30m with 25 Gbps or 40 Gbps.
Pricing:
If we talk about pricing, Cat 8 cables are more expensive than other standards, considering their unique features.
Shielding:
Both cables have shielding cable construction. Cat 7 cables offers extensive shielding for reduced attenuation. It requires special GigaGate45 connectors to fully take advantage of its higher performance features.
As Category 7 cables offer 1 100-meter 4-connector channel with shielded cabling, even if it operates at a higher frequency, there would be no improvement in data rate. Because 10GBase-T is still the fastest twisted pair-based data rate recognized by IEEE 802.3. Hence, even if a Category 7 cabling system is in your network, any available active equipment would have limitations of up to 10-Gbit/sec performance. It is not a recognized category by TIA.
Category 8 cables require shielded cabling. Unlike Cat5e to Cat6A, it has no unshielded twisted pair. The most likely cable construction for Category 8 will be 22-AWG S/FTP cabling.
Features Summary:
Pros and Cons:
Pros of Cat 7 Cables:
- Great for applications that require a lot of bandwidth, such as high-speed data transmission.
- Improved protection to minimize electromagnetic interference, guaranteeing consistent performance.
- Preparing for the future by ensuring compatibility with upcoming technologies such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond.
- Increased strength and durability due to thicker shielding and superior materials.
- Integration into networks is made seamless due to compatibility with current Ethernet standards.
- Appropriate for challenging environments, such as industrial and commercial surroundings.
- Enhanced signal-to-noise ratio leading to reliable and steady network connections.
Cons of Cat 7 Cables
- Higher cost compared to lower categories.
- Limited flexibility due to thicker shielding.
- Limited compatibility with older devices.
- Overkill for most home networking needs.
- Limited availability compared to Cat 5e or Cat 6.
Pros of Cat 8 Cables
- Data can be transferred at speeds of up to 40 gigabits per second.
- Increased data transfer capabilities for high-performance tasks.
- Enhanced immunity to electromagnetic interference.
- Enhanced readiness for changing network requirements.
- Enhanced capacity for extended cable distances in comparison to prior categories.
Cons of Cat8 Cables
- More expensive than earlier types of Ethernet cables.
- Restricted availability and limited compatibility with current hardware.
- Reduced maneuverability caused by thicker and less pliable cables.
- Greater vulnerability to disruption across extended distances.
- Specialized connectors and equipment are needed to achieve full performance.
Pick Your Choice!
These ethernet cables are modern-day products designed for cable-appropriate environments. Based on the feature comparison, you can choose a that fits your requirements and helps you render maximum data speed.
Still unsure which cable to choose? Post your question in the comment section below, and we’ll do our best to help you.